Mesaje on http://anonopsibero.blogspot.com/2011/11/anonymous-message-to-zeta-cartel.html
Monday, October 31, 2011
The Journalist from Mars
(a talk given at Fairness and Accuracy in Reporting's fifteenth anniversary celebration in New York City on January 23, 2002)
from the book
Media Control
by Noam Chomsky
Seven Stories Press, 2002
Sunday, October 30, 2011
struggleforfreedom80 videos
Videos to watch while taking a break from activism:
Noam Chomsky on Corporations being private tyrannies
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=iqlTyAMVDUk
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=mpd3grtjkK8
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=RxPUvQZ3rcQ
Noam Chomsky on today´s society and how to make changes:
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=2HvGy2gY0eM
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=MN2Q6sdh6Bg
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=27gfHU6G-hI
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=_cdSoMbwTA4
Noam Chomsky on where we go from here (at #Occupy Boston):
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=mHse0oaddr8
(Entire #Occupy Boston lecture + Q&A: http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=IZbNT62aprM&feature=related )
Alternatives to capitalism:
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=fJnX96id-xI
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=YDHBvQRyOr0
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=YftlB3AxBws
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Vu8J_UKKa-c
In debth:
Chomsky on today´s state-capitalist society, April 2011
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=iebK7VVDayY
Chomsky on Libertarian Socialism
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=kOTBGrrDeXg
Noam Chomsky on Corporations being private tyrannies
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=iqlTyAMVDUk
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=mpd3grtjkK8
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=RxPUvQZ3rcQ
Noam Chomsky on today´s society and how to make changes:
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=2HvGy2gY0eM
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=MN2Q6sdh6Bg
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=27gfHU6G-hI
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=_cdSoMbwTA4
Noam Chomsky on where we go from here (at #Occupy Boston):
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=mHse0oaddr8
(Entire #Occupy Boston lecture + Q&A: http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=IZbNT62aprM&feature=related )
Alternatives to capitalism:
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=fJnX96id-xI
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=YDHBvQRyOr0
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=YftlB3AxBws
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Vu8J_UKKa-c
In debth:
Chomsky on today´s state-capitalist society, April 2011
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=iebK7VVDayY
Chomsky on Libertarian Socialism
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=kOTBGrrDeXg
Saturday, October 29, 2011
How can I forget?
How can I forget?
How can I forget
That exploding sound
Which stole my family from me
Leaving me, with no one around?
How can I forget
Looking into mother's eyes?
Desperately, she called for my help
Hopelessly, I watched her die
How can I forget
The burnt bodies on the floor?
Whether my family was amongst them
Even today, I am unsure
How can I forget
Those piercing screams
Which haunt me daily
When appearing in my dreams?
How can I forget
How some are so unkind?
Peace on Earth is something
We urgently need to find
— Hashela Kumarawansa
How can I forget
That exploding sound
Which stole my family from me
Leaving me, with no one around?
How can I forget
Looking into mother's eyes?
Desperately, she called for my help
Hopelessly, I watched her die
How can I forget
The burnt bodies on the floor?
Whether my family was amongst them
Even today, I am unsure
How can I forget
Those piercing screams
Which haunt me daily
When appearing in my dreams?
How can I forget
How some are so unkind?
Peace on Earth is something
We urgently need to find
— Hashela Kumarawansa
Wednesday, October 26, 2011
11 Myths About Global Hunger
Myth 1: There isn’t enough food to feed the world.
Reality: There is enough food in the world today for everyone to have the nourishment necessary for a healthy and productive life. There is, however, a need to be more efficient, sustainable, and fair in how we grow and distribute food. This means supporting small-scale farmers – who make up the majority of farmers throughout the developing world – and ensuring that they have fair access to markets.
Reality: There is enough food in the world today for everyone to have the nourishment necessary for a healthy and productive life. There is, however, a need to be more efficient, sustainable, and fair in how we grow and distribute food. This means supporting small-scale farmers – who make up the majority of farmers throughout the developing world – and ensuring that they have fair access to markets.
Myth 2: Resolving hunger means ensuring people have enough to eat.
Reality: Hunger also involves the type of food you eat. Good nutrition means having the right combination of nutrients and calories needed for healthy development. It's especially important for infants, pregnant women and young children.
Reality: Hunger also involves the type of food you eat. Good nutrition means having the right combination of nutrients and calories needed for healthy development. It's especially important for infants, pregnant women and young children.
Myth 3: Droughts and other natural disasters are to blame for hunger.
Reality: Communities that build irrigation systems, storage facilities, and roads to connect them to markets are able to improve harvests. Then people can survive even during times of drought (Learn more). Nature is only one factor when it comes to hunger. The proportion of food crises that are linked to human causes has more than doubled since 1992. Conflict is often at the heart of today’s worst food crises.
Reality: Communities that build irrigation systems, storage facilities, and roads to connect them to markets are able to improve harvests. Then people can survive even during times of drought (Learn more). Nature is only one factor when it comes to hunger. The proportion of food crises that are linked to human causes has more than doubled since 1992. Conflict is often at the heart of today’s worst food crises.
Myth 4: Hunger exists when food is unavailable in shops and markets.
Reality: People can go hungry even when there's plenty of food around. Often it's a question of access - they can’t afford food or they can’t get to local markets. One way we can help is through cash transfers and electronic vouchers, which give people the ability to buy nutritious foods in local markets.
Reality: People can go hungry even when there's plenty of food around. Often it's a question of access - they can’t afford food or they can’t get to local markets. One way we can help is through cash transfers and electronic vouchers, which give people the ability to buy nutritious foods in local markets.
Myth 5: All of the world’s hungry live in Africa.
Reality: Of the world’s nearly one billion hungry, over half live in Asia and the Pacific (Hunger Stats). Hunger is also a relevant issue in the United States, where 50 million Americans are food insecure.
Reality: Of the world’s nearly one billion hungry, over half live in Asia and the Pacific (Hunger Stats). Hunger is also a relevant issue in the United States, where 50 million Americans are food insecure.
Myth 6: Too many people go hungry in my own country for me to worry about hunger abroad.
Reality: One in seven people in the world are hungry, which means one in seven people can’t create, study, or reach their full potential as human beings. That affects all of us. Hunger slows progress on other important areas that connect nations, including security.
Reality: One in seven people in the world are hungry, which means one in seven people can’t create, study, or reach their full potential as human beings. That affects all of us. Hunger slows progress on other important areas that connect nations, including security.
Myth 7: Hunger and famine are not easy to predict and can't be prepared for.
Reality: Tools exist to monitor and predict trends in food production as well as food prices. For example, the Famine Early Warning System Network (FEWS NET) analyzes meteorological and economic factors to alert the world to the possibility of hunger hotspots and famine.
Reality: Tools exist to monitor and predict trends in food production as well as food prices. For example, the Famine Early Warning System Network (FEWS NET) analyzes meteorological and economic factors to alert the world to the possibility of hunger hotspots and famine.
Myth 8: Hunger is basically a health issue.
Reality: This issue also affects education and the economy. Hungry children struggle to focus, learn, or even attend school. Without education, it's much harder for them to grow up and contribute to the growth of the national economy. A study in Guatemala found that boys who received fortified food before the age of three grew up to have wages 46 percent higher than those in a control group.
Reality: This issue also affects education and the economy. Hungry children struggle to focus, learn, or even attend school. Without education, it's much harder for them to grow up and contribute to the growth of the national economy. A study in Guatemala found that boys who received fortified food before the age of three grew up to have wages 46 percent higher than those in a control group.
Myth 9: People are only hungry during emergencies or disasters.
Reality: Emergencies only account for eight percent of the world’s hungry. There are close to one billion hungry people in the world who do not make the headlines and yet they go to bed hungry every night. This is why long-term efforts like school meals programmes are so important.
Reality: Emergencies only account for eight percent of the world’s hungry. There are close to one billion hungry people in the world who do not make the headlines and yet they go to bed hungry every night. This is why long-term efforts like school meals programmes are so important.
Myth 10: There are more pressing global issues than hunger.
Reality: When populations are hungry, economies suffer, people fight, and farmers can’t grow their crops effectively. We need to tackle hunger to be able to resolve environmental, economic, and security issues.
Reality: When populations are hungry, economies suffer, people fight, and farmers can’t grow their crops effectively. We need to tackle hunger to be able to resolve environmental, economic, and security issues.
Myth 11: There is nothing we can do to help hungry people.
Reality: There’s plenty we can do, even as individuals. Organizations like WFP need constant support and awareness-building efforts at the community level. You can help with that. Start where you are right now: online. Find us on Facebook and Twitter , and share our links to let your network know about the importance of hunger. And find out other ways to get involved here.
Reality: There’s plenty we can do, even as individuals. Organizations like WFP need constant support and awareness-building efforts at the community level. You can help with that. Start where you are right now: online. Find us on Facebook and Twitter , and share our links to let your network know about the importance of hunger. And find out other ways to get involved here.
(This article was produced in conjunction with dosomething.org)
Monday, October 24, 2011
the New York City General Assembly occupying Wall Street in Liberty Square, urge you to assert your power
Current TV, Keith Olbermann, 05/10/2011.
Declaration of the Occupation of New York City
Declaration of the Occupation of New York City
As we gather together in solidarity to express a feeling of mass injustice, we must not lose sight of what brought us together. We write so that all people who feel wronged by the corporate forces of the world can know that we are your allies.
As one people, united, we acknowledge the reality: that the future of the human race requires the cooperation of its members; that our system must protect our rights, and upon corruption of that system, it is up to the individuals to protect their own rights, and those of their neighbors; that a democratic government derives its just power from the people, but corporations do not seek consent to extract wealth from the people and the Earth; and that no true democracy is attainable when the process is determined by economic power. We come to you at a time when corporations, which place profit over people, self-interest over justice, and oppression over equality, run our governments. We have peaceably assembled here, as is our right, to let these facts be known.
They have taken our houses through an illegal foreclosure process, despite not having the original mortgage.
They have taken bailouts from taxpayers with impunity, and continue to give Executives exorbitant bonuses.
They have perpetuated inequality and discrimination in the workplace based on age, the color of one’s skin, sex, gender identity and sexual orientation.
They have poisoned the food supply through negligence, and undermined the farming system through monopolization.
They have profited off of the torture, confinement, and cruel treatment of countless nonhuman animals, and actively hide these practices.
They have continuously sought to strip employees of the right to negotiate for better pay and safer working conditions.
They have held students hostage with tens of thousands of dollars of debt on education, which is itself a human right.
They have consistently outsourced labor and used that outsourcing as leverage to cut workers’ healthcare and pay.
They have influenced the courts to achieve the same rights as people, with none of the culpability or responsibility.
They have spent millions of dollars on legal teams that look for ways to get them out of contracts in regards to health insurance.
They have sold our privacy as a commodity.
They have used the military and police force to prevent freedom of the press.
They have deliberately declined to recall faulty products endangering lives in pursuit of profit.
They determine economic policy, despite the catastrophic failures their policies have produced and continue to produce.
They have donated large sums of money to politicians supposed to be regulating them.
They continue to block alternate forms of energy to keep us dependent on oil.
They continue to block generic forms of medicine that could save people’s lives in order to protect investments that have already turned a substantive profit.
They have purposely covered up oil spills, accidents, faulty bookkeeping, and inactive ingredients in pursuit of profit.
They purposefully keep people misinformed and fearful through their control of the media.
They have accepted private contracts to murder prisoners even when presented with serious doubts about their guilt.
They have perpetuated colonialism at home and abroad.
They have participated in the torture and murder of innocent civilians overseas.
They continue to create weapons of mass destruction in order to receive government contracts.*
To the people of the world,
We, the New York City General Assembly occupying Wall Street in Liberty Square, urge you to assert your power.
Exercise your right to peaceably assemble; occupy public space; create a process to address the problems we face, and generate solutions accessible to everyone.
To all communities that take action and form groups in the spirit of direct democracy, we offer support, documentation, and all of the resources at our disposal.
Join us and make your voices heard!
*These grievances are not all-inclusive.
Sunday, October 23, 2011
Homage to Catalonia
Title: Homage to Catalonia (1938)
Author: George Orwell
*
Answer not a fool according to his folly, lest thou be like unto him.
Answer a fool according to his folly, lest he be wise in his own conceit.
--Proverbs XXVI. 5-6
*
Author: George Orwell
*
Answer not a fool according to his folly, lest thou be like unto him.
Answer a fool according to his folly, lest he be wise in his own conceit.
--Proverbs XXVI. 5-6
*
Saturday, October 22, 2011
B Movie plot, what's the sequel?; Analysts question that the Quds force would behave as the US government claims
Given the power struggle pitting Khamenei and his supporters against Ahmadinejad and his camp, and given the extreme hostility that some former Ahmadinejad supporters have toward him and their fear that he might be able to establish some form of diplomatic relations with the United States, the possibility of such a rogue operation cannot be discarded. But the indictment against Arbabsiar and Shakuri claims that they are members of the Quds force, and given the discipline that the Quds force has demonstrated in its operations throughout the Middle East, I still find it difficult to believe that they would embark on what seems to be a useless, dangerous, and relatively easy-to-discover operation.
Thus, at this point, I find the claim that the IRI was involved in the plot highly unlikely. The more information that becomes available, the more it appears like a frame-up of Manssor Arbabsiar, a classic case of entrapment. But, once again, there is nothing the IRI might do that would surprise me.
Read more: http://www.pbs.org/wgbh/pages/frontline/tehranbureau/2011/10/post-6.html#ixzz1aiKULJZg
We need to worry. What is this a pretext for?
http://www.pbs.org/wgbh/pages/frontline/tehranbureau/2011/10/post-6.html
There is a small chance that some rogue elements in the Revolutionary Guards decided to carry out such a plot. There is precedence for such an operation. During Akbar Hashemi Rafsanjani's second term as president, rogue elements of the Ministry of Intelligence led by Saeed Emami -- leader of the gang that assassinated numerous dissidents in what is now known as the infamous Chain Murders -- tried to smuggle missiles out of Iran to Brussels to attack the NATO headquarters. The plot was discovered, and Rafsanjani later acknowledged it. Its discovery set back relations between Iran and the European Union for several years.
Thus, at this point, I find the claim that the IRI was involved in the plot highly unlikely. The more information that becomes available, the more it appears like a frame-up of Manssor Arbabsiar, a classic case of entrapment. But, once again, there is nothing the IRI might do that would surprise me.
Read more: http://www.pbs.org/wgbh/pages/frontline/tehranbureau/2011/10/post-6.html#ixzz1aiKULJZg
We need to worry. What is this a pretext for?
http://www.pbs.org/wgbh/pages/frontline/tehranbureau/2011/10/post-6.html
There is a small chance that some rogue elements in the Revolutionary Guards decided to carry out such a plot. There is precedence for such an operation. During Akbar Hashemi Rafsanjani's second term as president, rogue elements of the Ministry of Intelligence led by Saeed Emami -- leader of the gang that assassinated numerous dissidents in what is now known as the infamous Chain Murders -- tried to smuggle missiles out of Iran to Brussels to attack the NATO headquarters. The plot was discovered, and Rafsanjani later acknowledged it. Its discovery set back relations between Iran and the European Union for several years.
fish production in Iraq
By Mohammad Raafi, FAO - Iraq
Soaring food prices, coupled with years of conflict and economic sanctions, have had a devastating impact on the livelihoods of Iraq’s people. To help mitigate the effects accompanying the outbreak of the avian flu, along with the rising prices of poultry, FAO sought to introduce an alternative source of protein to Iraqi household diets by helping increase fish production.
The fishing sector is among the weakest in Iraq’s economy. The country has a small coastline of less than 60 km. The rivers Tigris and Euphrates as well as the country’s marshes, dams and reservoirs, make up Iraq’s main water source for inland fishing.
The per capita fish consumption in Iraq is the lowest in the region compared to 12 kg in the Gulf Cooperation Countries, 10 kg in Iran, 4.5 kg in Syria and 3.7 kg in Jordan. The per capita fish consumption in Iraq saw a decline from 2.5 kg in 1990 to 0.8 kg in 2005. This was not only due to a decrease in purchasing power, but also to a gap between current supply and demand USAID, Business Models for Aquaculture in Iraq, May 2006.
In Iraq, this industry relies mostly on inland fishing which faces several constraints such as the lack of quality fish seed reaching the areas where there is potential for inland fish production. Poor communication and transportation facilities further aggravate the problem.
Since 2004, FAO, in partnership with Iraq’s Ministry of Agriculture, has implemented a number of projects to restore and develop fish production in the country. Through the United Nations Development Group Iraq Trust Fund, FAO has contributed US $10 million towards the fisheries sector. These projects have sought to develop the current state of aquaculture by training and transferring the most recent technology in cage fish culture and by encouraging sustainable aquaculture activities using both local and foreign species.
The Organization has helped increase inland fish production through management, stocking and enhancement of the diversity of species with an effective regulatory framework. The project includes a range of interventions, such as the establishment of brood stock development centres and a brood fish supply network, the diversification of species in inland fish production and the establishment of a decentralized fish seed supply network.
The ultimate beneficiaries of this project are the inland fisheries and farming communities, particularly the rural poor and marginalized segments of society. It is estimated that to date more than 9,000 Iraqis benefited from the results of these projects. FAO, 2011 Project Summary, July 2011
With FAO installing cages for fish harvesting in twelve different locations in the Euphrates and Tigris, locally harvested fish prices have dropped by 40 per cent according to an evaluation conducted jointly by FAO and local universities. Basra University, Mosul University 2010 The growth period of fish also dropped from eight months to four.
These results have encouraged the private sector in Iraq to adopt the same technology as it has the potential to increase the pace of the rehabilitation of the fisheries sector. It equally enhanced the role of the Ministry of Agriculture to boost the private sector’s investments in this field, while leading to the establishment of 12 fishery associations.
Soaring food prices, coupled with years of conflict and economic sanctions, have had a devastating impact on the livelihoods of Iraq’s people. To help mitigate the effects accompanying the outbreak of the avian flu, along with the rising prices of poultry, FAO sought to introduce an alternative source of protein to Iraqi household diets by helping increase fish production.
The fishing sector is among the weakest in Iraq’s economy. The country has a small coastline of less than 60 km. The rivers Tigris and Euphrates as well as the country’s marshes, dams and reservoirs, make up Iraq’s main water source for inland fishing.
The per capita fish consumption in Iraq is the lowest in the region compared to 12 kg in the Gulf Cooperation Countries, 10 kg in Iran, 4.5 kg in Syria and 3.7 kg in Jordan. The per capita fish consumption in Iraq saw a decline from 2.5 kg in 1990 to 0.8 kg in 2005. This was not only due to a decrease in purchasing power, but also to a gap between current supply and demand USAID, Business Models for Aquaculture in Iraq, May 2006.
In Iraq, this industry relies mostly on inland fishing which faces several constraints such as the lack of quality fish seed reaching the areas where there is potential for inland fish production. Poor communication and transportation facilities further aggravate the problem.
Since 2004, FAO, in partnership with Iraq’s Ministry of Agriculture, has implemented a number of projects to restore and develop fish production in the country. Through the United Nations Development Group Iraq Trust Fund, FAO has contributed US $10 million towards the fisheries sector. These projects have sought to develop the current state of aquaculture by training and transferring the most recent technology in cage fish culture and by encouraging sustainable aquaculture activities using both local and foreign species.
The Organization has helped increase inland fish production through management, stocking and enhancement of the diversity of species with an effective regulatory framework. The project includes a range of interventions, such as the establishment of brood stock development centres and a brood fish supply network, the diversification of species in inland fish production and the establishment of a decentralized fish seed supply network.
The ultimate beneficiaries of this project are the inland fisheries and farming communities, particularly the rural poor and marginalized segments of society. It is estimated that to date more than 9,000 Iraqis benefited from the results of these projects. FAO, 2011 Project Summary, July 2011
With FAO installing cages for fish harvesting in twelve different locations in the Euphrates and Tigris, locally harvested fish prices have dropped by 40 per cent according to an evaluation conducted jointly by FAO and local universities. Basra University, Mosul University 2010 The growth period of fish also dropped from eight months to four.
These results have encouraged the private sector in Iraq to adopt the same technology as it has the potential to increase the pace of the rehabilitation of the fisheries sector. It equally enhanced the role of the Ministry of Agriculture to boost the private sector’s investments in this field, while leading to the establishment of 12 fishery associations.
child survival crisis in the Horn of Africa
UNICEF report: Crisis in the Horn of Africa far from over
NAIROBI, Kenya, 20 October 2011 – The massive international response to the child survival crisis in the Horn of Africa has already shown some positive results, but much more needs to be done to save hundreds of thousands of children at risk of dying from malnutrition and disease, UNICEF said today according to a progress report three months after famine was declared in parts of Somalia.
See the full report here [PDF]
”We have saved many children, in Somalia, in the refugee camps in neighbouring countries as well as in the other regions in Kenya, Ethiopia and Djibouti hit by prolonged drought, escalating food prices and conflict,” said Elhadj As Sy, UNICEF Regional Director for Eastern and Southern Africa, releasing the report: Response to the Horn of Africa Emergency.
See the full report here [PDF]
”We have saved many children, in Somalia, in the refugee camps in neighbouring countries as well as in the other regions in Kenya, Ethiopia and Djibouti hit by prolonged drought, escalating food prices and conflict,” said Elhadj As Sy, UNICEF Regional Director for Eastern and Southern Africa, releasing the report: Response to the Horn of Africa Emergency.
the prognosis for economic recovery
| Continued economic stagnation in Europe and the United States, along with renewed uncertainty about the health of the debt-ridden global financial system, has been raising fresh concerns about the prognosis for economic recovery and even the potential for a relapse into crisis. A big part of the problem, as Harvard economist Kenneth Rogoff pointed out in This Time Is Different: Eight Centuries of Financial Folly (Princeton University Press, September 2009), the best-selling academic book he coauthored with fellow economist Carmen Reinhart, is that we are working through a recession linked to a deep financial crisis—a powerful amplifying mechanism with long-lasting effects. Reinhart and Rogoff’s work, based on investigations of empirical data from 800 years of financial crises, shows that such downturns are exceptionally deep and long lasting, as well as unprecedented in the United States since World War II. McKinsey’s Bill Javetski and Tim Koller recently visited Rogoff in his Cambridge, Massachusetts, office to ask where we are in the recovery time line and why Rogoff thinks that a bout of moderate inflation may help the world regain economic health. Rogoff’s outlook—that the balance of current economic risks tilts “more to the downside than the upside”—is sobering but essential reading for business leaders and policy makers trying to make sense of today’s uncertain environment. |
Friday, October 21, 2011
Sue me if you dare
Public anger at the Chinese regime’s elite class erupted last month after this deadly hit-and-run accident at Hebei University in northern China. The driver is the son of a high-ranking police officer. He drove off after running down two students. When crowds stopped his car, he reportedly shouted “Sue me if you dare, my father is Li Gang.”
In the evening on October 16, 2010, due to drunk driving and speeding, a black Volkswagen Magotan hit 2 female student pedestrians wearing roller shoes in front of a supermarket at Hebei University. The incident caused one death and one injured. After the incident, like nothing had happened, the driver continued to drive his girlfriend to school. He was then later stopped by number of students and school security guards on his way back. Surprisingly, the young man showed little remorse and fear, he shouted, “Go ahead, sue me if you dare, my dad is Li Gang”. The report of this incident immediately caused uproar in China’s online community.
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Li_Gang_incident
Near Wenzhou's No.14 Middle School on West Jiangbin Road (江滨西路) two nights ago at around 10pm, 19-year-old Ma Wenzong (马文总) assaulted the 18-month-old daughter of a shopkeeper during an altercation involving his Mercedes Benz GL450 SUV. While a bystander tried to block the path of the vehicle, Ma shouted out "My dad is the mayor!" (我爸是市长!), enraging the assembled onlookers in what looks to be the second Rich Brat Who Can't Drive Incident in one week.
The incident reportedly began when Ma's Mercedes SUV crushed the storefront signage of shopkeeper Liu Xiuying (刘秀英). After the two exchanged words, Ma rushed into Liu's store, and smashed a landline phone that sat atop a counter on the ground, before then using the store's calculator to repeatedly smack the head of Liu's 18-month-old daughter until blood was drawn.
At this point, Ma panicked and tried to escape in his SUV, but was blocked by bystander Wu Xiaodan (吴哓丹), who demanded that Ma "explain himself". Ma responded by attempting to drive away, and caught Wu's thigh underneath a wheel. Witnesses report that the SUV then reversed over Wu's thigh after rolling over it the first time.
10 bystanders then came out and surrounded the vehicle, whereupon he shouted the five characters that he'll forever be known for. Police eventually arrived, only to leave promptly after declaring both Ma and his girlfriend, who was in the vehicle during the entire incident, were not driving drunk.
The apparent failure to administer justice enraged the gathered onlookers, who at this point coalesced into a mob of a hundred or so people that surrounded Ma and demanded that he undergo further blood tests to determine whether he'd been drunk. Extra police were required to disperse the crowd, who were eventually appeased after authorities arrived four and a half hours after calls for a blood test were first made. Ma was then whisked away to a local police station, and is currently under detention in Wenzhou's Lucheng district (鹿城区).
Wu Xiaodan suffered multiple fractures in his leg after being run over by Ma's Mercedes, and Liu's Xiuying's daughter looks to be in stable condition, judging by photographs taken at scene following the incident.
Meanwhile, it was revealed later that Ma is merely the son of a local businessman, rather than Zhao Yide (赵一德), the Mayor of Wenzhou.
It doesn't come as much of surprise that a 19-year-old was cruising around with a GL450, which has a modest sticker price that hovers in the neighborhood of 1.5 million RMB ($235,000 USD) for the 2011 model. Wenzhou and the rest of Zhejiang are known for having their fair share of wealthy types who splurge on cars, with an accident in 2009 involving a 20-year-old Porsche driver highlighting the extent to which kids had it made in the wealthy coastal province.
We think it's a good thing that Ma doesn't lack for testicular fortitude, given his willingness to tell blatant lies and attack infant children. That sort of moxie should certainly serve him well when the cell door slams shuts in his face for the long haul.
October 13, 2011,Guangzhou, China.. A little girl, about 2 years old, was hit by a truck in a car accident. She was run over three or more times. Around 18 passer bys walked around the body without helping or calling for help. Finally a women took the body out of the road and called the mother. The incident is sparking outrage in China and prompting soul-searching over why people didn’t help the child.
http://www.washingtonpost.com/world/asia_pacific/an-injured-toddler-is-ignored-and-chinese-ask-why/2011/10/19/gIQAxhnpxL_story.html?tid=sm_btn_twitter
Tuesday, October 18, 2011
Sunday, October 16, 2011
Saturday, October 15, 2011
all American troops will leave except for about 160 troops attached to the US Embassy in Baghdad
The US is abandoning plans to keep troops in Iraq past a year-end withdrawal deadline, The Associated Press reported.
The decision to pull out fully by January will effectively end more than eight years of US involvement in the Iraq war, despite ongoing concerns about its security forces and the potential for instability.
A senior administration official in Washington confirmed on Saturday that all American troops will leave except for about 160 troops attached to the US Embassy in Baghdad.
Under a 2008 security agreement, all US forces- over 40,000 on Iraqi soil now- are required to leave by the end of 2011.
But the Pentagon, for months, had been debating whether to leave up to 5,000 troops to train security forces and hinder Iranian influence.
The senior US military official said the withdrawal could allow future, limited US military training missions if requested.
Throughout the months of negotiations, Iraqi political leaders have rejected giving legal immunity to US troops, a deal-breaker to Washington.
The decision to pull out fully by January will effectively end more than eight years of US involvement in the Iraq war, despite ongoing concerns about its security forces and the potential for instability.
A senior administration official in Washington confirmed on Saturday that all American troops will leave except for about 160 troops attached to the US Embassy in Baghdad.
Under a 2008 security agreement, all US forces- over 40,000 on Iraqi soil now- are required to leave by the end of 2011.
But the Pentagon, for months, had been debating whether to leave up to 5,000 troops to train security forces and hinder Iranian influence.
The senior US military official said the withdrawal could allow future, limited US military training missions if requested.
Throughout the months of negotiations, Iraqi political leaders have rejected giving legal immunity to US troops, a deal-breaker to Washington.
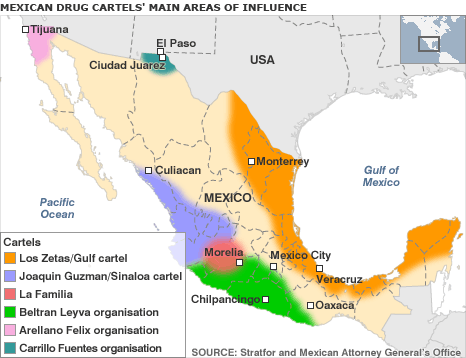
violence in Mexican prison
A bloody, hours-long fight in a prison in the Mexican border city of Matamoros has left 20 inmates dead and 12 injured, state officials have said.
The fight reportedly started as a dispute between two inmates and other prisoners joined in, creating a melee that lasted until authorities retook control of the prison facility in the town, which sits across the border from Brownsville, Texas.
A statement from state public security department in Tamaulipas, where Matamoros is located, said officials were notifying the families of those killed and injured. It said there would be an investigation.
The violence lasted from about 8h00 to 10h30am local time before soldiers and marines took control, according to a state official who was not authorised to comment.
The violence comes as Mexican prison conditions have been under increased scrutiny because of violence and escapes.
On Thursday, a fight between gang members at a prison outside Monterrey left seven inmates dead.
In July, a riot in a prison in the border city of Juarez killed 17 inmates.
Gangs and drug cartels often dispute for control of prisons in Mexico, which also suffer a high level of corruption.
The fight reportedly started as a dispute between two inmates and other prisoners joined in, creating a melee that lasted until authorities retook control of the prison facility in the town, which sits across the border from Brownsville, Texas.
A statement from state public security department in Tamaulipas, where Matamoros is located, said officials were notifying the families of those killed and injured. It said there would be an investigation.
The violence lasted from about 8h00 to 10h30am local time before soldiers and marines took control, according to a state official who was not authorised to comment.
The violence comes as Mexican prison conditions have been under increased scrutiny because of violence and escapes.
On Thursday, a fight between gang members at a prison outside Monterrey left seven inmates dead.
In July, a riot in a prison in the border city of Juarez killed 17 inmates.
Gangs and drug cartels often dispute for control of prisons in Mexico, which also suffer a high level of corruption.
George Orwell: Notes on Nationalism
Somewhere or other Byron makes use of the French word longeur, and remarks in passing that though in England we happen not to have the word, we have the thing in considerable profusion. In the same way, there is a habit of mind which is now so widespread that it affects our thinking on nearly every subject, but which has not yet been given a name. As the nearest existing equivalent I have chosen the word ‘nationalism’, but it will be seen in a moment that I am not using it in quite the ordinary sense, if only because the emotion I am speaking about does not always attach itself to what is called a nation — that is, a single race or a geographical area. It can attach itself to a church or a class, or it may work in a merely negative sense, against something or other and without the need for any positive object of loyalty.
By ‘nationalism’ I mean first of all the habit of assuming that human beings can be classified like insects and that whole blocks of millions or tens of millions of people can be confidently labelled ‘good’ or ‘bad’(1). But secondly — and this is much more important — I mean the habit of identifying oneself with a single nation or other unit, placing it beyond good and evil and recognising no other duty than that of advancing its interests. Nationalism is not to be confused with patriotism. Both words are normally used in so vague a way that any definition is liable to be challenged, but one must draw a distinction between them, since two different and even opposing ideas are involved. By ‘patriotism’ I mean devotion to a particular place and a particular way of life, which one believes to be the best in the world but has no wish to force on other people. Patriotism is of its nature defensive, both militarily and culturally. Nationalism, on the other hand, is inseparable from the desire for power. The abiding purpose of every nationalist is to secure more power and more prestige, not for himself but for the nation or other unit in which he has chosen to sink his own individuality.
So long as it is applied merely to the more notorious and identifiable nationalist movements in Germany, Japan, and other countries, all this is obvious enough. Confronted with a phenomenon like Nazism, which we can observe from the outside, nearly all of us would say much the same things about it. But here I must repeat what I said above, that I am only using the word ‘nationalism’ for lack of a better. Nationalism, in the extended sense in which I am using the word, includes such movements and tendencies as Communism, political Catholicism, Zionism, Antisemitism, Trotskyism and Pacifism. It does not necessarily mean loyalty to a government or a country, still less to one's own country, and it is not even strictly necessary that the units in which it deals should actually exist. To name a few obvious examples, Jewry, Islam, Christendom, the Proletariat and the White Race are all of them objects of passionate nationalistic feeling: but their existence can be seriously questioned, and there is no definition of any one of them that would be universally accepted.
It is also worth emphasising once again that nationalist feeling can be purely negative. There are, for example, Trotskyists who have become simply enemies of the U.S.S.R. without developing a corresponding loyalty to any other unit. When one grasps the implications of this, the nature of what I mean by nationalism becomes a good deal clearer. A nationalist is one who thinks solely, or mainly, in terms of competitive prestige. He may be a positive or a negative nationalist — that is, he may use his mental energy either in boosting or in denigrating — but at any rate his thoughts always turn on victories, defeats, triumphs and humiliations. He sees history, especially contemporary history, as the endless rise and decline of great power units, and every event that happens seems to him a demonstration that his own side is on the upgrade and some hated rival is on the downgrade. But finally, it is important not to confuse nationalism with mere worship of success. The nationalist does not go on the principle of simply ganging up with the strongest side. On the contrary, having picked his side, he persuades himself that it is the strongest, and is able to stick to his belief even when the facts are overwhelmingly against him. Nationalism is power-hunger tempered by self-deception. Every nationalist is capable of the most flagrant dishonesty, but he is also — since he is conscious of serving something bigger than himself — unshakeably certain of being in the right.
Now that I have given this lengthy definition, I think it will be admitted that the habit of mind I am talking about is widespread among the English intelligentsia, and more widespread there than among the mass of the people. For those who feel deeply about contemporary politics, certain topics have become so infected by considerations of prestige that a genuinely rational approach to them is almost impossible. Out of the hundreds of examples that one might choose, take this question: Which of the three great allies, the U.S.S.R., Britain and the USA, has contributed most to the defeat of Germany? In theory, it should be possible to give a reasoned and perhaps even a conclusive answer to this question. In practice, however, the necessary calculations cannot be made, because anyone likely to bother his head about such a question would inevitably see it in terms of competitive prestige. He would therefore start by deciding in favour of Russia, Britain or America as the case might be, and only after this would begin searching for arguments that seemed to support his case. And there are whole strings of kindred questions to which you can only get an honest answer from someone who is indifferent to the whole subject involved, and whose opinion on it is probably worthless in any case. Hence, partly, the remarkable failure in our time of political and military prediction. It is curious to reflect that out of al the ‘experts’ of all the schools, there was not a single one who was able to foresee so likely an event as the Russo-German Pact of 1939(2). And when news of the Pact broke, the most wildly divergent explanations were of it were given, and predictions were made which were falsified almost immediately, being based in nearly every case not on a study of probabilities but on a desire to make the U.S.S.R. seem good or bad, strong or weak. Political or military commentators, like astrologers, can survive almost any mistake, because their more devoted followers do not look to them for an appraisal of the facts but for the stimulation of nationalistic loyalties(3). And aesthetic judgements, especially literary judgements, are often corrupted in the same way as political ones. It would be difficult for an Indian Nationalist to enjoy reading Kipling or for a Conservative to see merit in Mayakovsky, and there is always a temptation to claim that any book whose tendency one disagrees with must be a bad book from a literary point of view. People of strongly nationalistic outlook often perform this sleight of hand without being conscious of dishonesty.
In England, if one simply considers the number of people involved, it is probable that the dominant form of nationalism is old-fashioned British jingoism. It is certain that this is still widespread, and much more so than most observers would have believed a dozen years ago. However, in this essay I am concerned chiefly with the reactions of the intelligentsia, among whom jingoism and even patriotism of the old kind are almost dead, though they now seem to be reviving among a minority. Among the intelligentsia, it hardly needs saying that the dominant form of nationalism is Communism — using this word in a very loose sense, to include not merely Communist Party members, but ‘fellow travellers’ and russophiles generally. A Communist, for my purpose here, is one who looks upon the U.S.S.R. as his Fatherland and feels it his duty t justify Russian policy and advance Russian interests at all costs. Obviously such people abound in England today, and their direct and indirect influence is very great. But many other forms of nationalism also flourish, and it is by noticing the points of resemblance between different and even seemingly opposed currents of thought that one can best get the matter into perspective.
Ten or twenty years ago, the form of nationalism most closely corresponding to Communism today was political Catholicism. Its most outstanding exponent — though he was perhaps an extreme case rather than a typical one — was G. K. Chesterton. Chesterton was a writer of considerable talent who whose to suppress both his sensibilities and his intellectual honesty in the cause of Roman Catholic propaganda. During the last twenty years or so of his life, his entire output was in reality an endless repetition of the same thing, under its laboured cleverness as simple and boring as ‘Great is Diana of the Ephesians.’ Every book that he wrote, every scrap of dialogue, had to demonstrate beyond the possibility of mistake the superiority of the Catholic over the Protestant or the pagan. But Chesterton was not content to think of this superiority as merely intellectual or spiritual: it had to be translated into terms of national prestige and military power, which entailed an ignorant idealisation of the Latin countries, especially France. Chesterton had not lived long in France, and his picture of it — as a land of Catholic peasants incessantly singing the Marseillaise over glasses of red wine — had about as much relation to reality as Chu Chin Chow has to everyday life in Baghdad. And with this went not only an enormous overestimation of French military power (both before and after 1914-18 he maintained that France, by itself, was stronger than Germany), but a silly and vulgar glorification of the actual process of war. Chesterton's battle poems, such as Lepanto or The Ballad of Saint Barbara, make The Charge of the Light Brigade read like a pacifist tract: they are perhaps the most tawdry bits of bombast to be found in our language. The interesting thing is that had the romantic rubbish which he habitually wrote about France and the French army been written by somebody else about Britain and the British army, he would have been the first to jeer. In home politics he was a Little Englander, a true hater of jingoism and imperialism, and according to his lights a true friend of democracy. Yet when he looked outwards into the international field, he could forsake his principles without even noticing he was doing so. Thus, his almost mystical belief in the virtues of democracy did not prevent him from admiring Mussolini. Mussolini had destroyed the representative government and the freedom of the press for which Chesterton had struggled so hard at home, but Mussolini was an Italian and had made Italy strong, and that settled the matter. Nor did Chesterton ever find a word to say about imperialism and the conquest of coloured races when they were practised by Italians or Frenchmen. His hold on reality, his literary taste, and even to some extent his moral sense, were dislocated as soon as his nationalistic loyalties were involved.
Obviously there are considerable resemblances between political Catholicism, as exemplified by Chesterton, and Communism. So there are between either of these and for instance Scottish nationalism, Zionism, Antisemitism or Trotskyism. It would be an oversimplification to say that all forms of nationalism are the same, even in their mental atmosphere, but there are certain rules that hold good in all cases. The following are the principal characteristics of nationalist thought:
Obsession. As nearly as possible, no nationalist ever thinks, talks, or writes about anything except the superiority of his own power unit. It is difficult if not impossible for any nationalist to conceal his allegiance. The smallest slur upon his own unit, or any implied praise of a rival organization, fills him with uneasiness which he can relieve only by making some sharp retort. If the chosen unit is an actual country, such as Ireland or India, he will generally claim superiority for it not only in military power and political virtue, but in art, literature, sport, structure of the language, the physical beauty of the inhabitants, and perhaps even in climate, scenery and cooking. He will show great sensitiveness about such things as the correct display of flags, relative size of headlines and the order in which different countries are named(4). Nomenclature plays a very important part in nationalist thought. Countries which have won their independence or gone through a nationalist revolution usually change their names, and any country or other unit round which strong feelings revolve is likely to have several names, each of them carrying a different implication. The two sides of the Spanish Civil War had between them nine or ten names expressing different degrees of love and hatred. Some of these names (e. g. ‘Patriots’ for Franco-supporters, or ‘Loyalists’ for Government-supporters) were frankly question-begging, and there was no single one of the which the two rival factions could have agreed to use. All nationalists consider it a duty to spread their own language to the detriment of rival languages, and among English-speakers this struggle reappears in subtler forms as a struggle between dialects. Anglophobe-Americans will refuse to use a slang phrase if they know it to be of British origin, and the conflict between Latinizers and Germanizers often has nationalists motives behind it. Scottish nationalists insist on the superiority of Lowland Scots, and socialists whose nationalism takes the form of class hatred tirade against the B.B.C. accent and even the often gives the impression of being tinged by belief in symphatetic magic — a belief which probably comes out in the widespread custom of burning political enemies in effigy, or using pictures of them as targets in shooting galleries.
Instability. The intensity with which they are held does not prevent nationalist loyalties from being transferable. To begin with, as I have pointed out already, they can be and often are fastened up on some foreign country. One quite commonly finds that great national leaders, or the founders of nationalist movements, do not even belong to the country they have glorified. Sometimes they are outright foreigners, or more often they come from peripheral areas where nationality is doubtful. Examples are Stalin, Hitler, Napoleon, de Valera, Disraeli, Poincare, Beaverbrook. The Pan-German movement was in part the creation of an Englishman, Houston Chamberlain. For the past fifty or a hundred years, transferred nationalism has been a common phenomenon among literary intellectuals. With Lafcadio Hearne the transference was to Japan, with Carlyle and many others of his time to Germany, and in our own age it is usually to Russia. But the peculiarly interesting fact is that re-transference is also possible. A country or other unit which has been worshipped for years may suddenly become detestable, and some other object of affection may take its place with almost no interval. In the first version of H. G. Wells's Outline of History, and others of his writings about that time, one finds the United States praised almost as extravagantly as Russia is praised by Communists today: yet within a few years this uncritical admiration had turned into hostility. The bigoted Communist who changes in a space of weeks, or even days, into an equally bigoted Trotskyist is a common spectacle. In continental Europe Fascist movements were largely recruited from among Communists, and the opposite process may well happen within the next few years. What remains constant in the nationalist is his state of mind: the object of his feelings is changeable, and may be imaginary.
But for an intellectual, transference has an important function which I have already mentioned shortly in connection with Chesterton. It makes it possible for him to be much more nationalistic — more vulgar, more silly, more malignant, more dishonest — that he could ever be on behalf of his native country, or any unit of which he had real knowledge. When one sees the slavish or boastful rubbish that is written about Stalin, the Red Army, etc. by fairly intelligent and sensitive people, one realises that this is only possible because some kind of dislocation has taken place. In societies such as ours, it is unusual for anyone describable as an intellectual to feel a very deep attachment to his own country. Public opinion — that is, the section of public opinion of which he as an intellectual is aware — will not allow him to do so. Most of the people surrounding him are sceptical and disaffected, and he may adopt the same attitude from imitativeness or sheer cowardice: in that case he will have abandoned the form of nationalism that lies nearest to hand without getting any closer to a genuinely internationalist outlook. He still feels the need for a Fatherland, and it is natural to look for one somewhere abroad. Having found it, he can wallow unrestrainedly in exactly those emotions from which he believes that he has emancipated himself. God, the King, the Empire, the Union Jack — all the overthrown idols can reappear under different names, and because they are not recognised for what they are they can be worshipped with a good conscience. Transferred nationalism, like the use of scapegoats, is a way of attaining salvation without altering one's conduct.
Indifference to Reality. All nationalists have the power of not seeing resemblances between similar sets of facts. A British Tory will defend self-determination in Europe and oppose it in India with no feeling of inconsistency. Actions are held to be good or bad, not on their own merits, but according to who does them, and there is almost no kind of outrage — torture, the use of hostages, forced labour, mass deportations, imprisonment without trial, forgery, assassination, the bombing of civilians — which does not change its moral colour when it is committed by ‘our’ side. The Liberal News Chronicle published, as an example of shocking barbarity, photographs of Russians hanged by the Germans, and then a year or two later published with warm approval almost exactly similar photographs of Germans hanged by the Russians(5). It is the same with historical events. History is thought of largely in nationalist terms, and such things as the Inquisition, the tortures of the Star Chamber, the exploits of the English buccaneers (Sir Francis Drake, for instance, who was given to sinking Spanish prisoners alive), the Reign of Terror, the heroes of the Mutiny blowing hundreds of Indians from the guns, or Cromwell's soldiers slashing Irishwomen's faces with razors, become morally neutral or even meritorious when it is felt that they were done in the ‘right’ cause. If one looks back over the past quarter of a century, one finds that there was hardly a single year when atrocity stories were not being reported from some part of the world; and yet in not one single case were these atrocities — in Spain, Russia, China, Hungary, Mexico, Amritsar, Smyrna — believed in and disapproved of by the English intelligentsia as a whole. Whether such deeds were reprehensible, or even whether they happened, was always decided according to political predilection.
The nationalist not only does not disapprove of atrocities committed by his own side, but he has a remarkable capacity for not even hearing about them. For quite six years the English admirers of Hitler contrived not to learn of the existence of Dachau and Buchenwald. And those who are loudest in denouncing the German concentration camps are often quite unaware, or only very dimly aware, that there are also concentration camps in Russia. Huge events like the Ukraine famine of 1933, involving the deaths of millions of people, have actually escaped the attention of the majority of English russophiles. Many English people have heard almost nothing about the extermination of German and Polish Jews during the present war. Their own antisemitism has caused this vast crime to bounce off their consciousness. In nationalist thought there are facts which are both true and untrue, known and unknown. A known fact may be so unbearable that it is habitually pushed aside and not allowed to enter into logical processes, or on the other hand it may enter into every calculation and yet never be admitted as a fact, even in one's own mind.
Every nationalist is haunted by the belief that the past can be altered. He spends part of his time in a fantasy world in which things happen as they should — in which, for example, the Spanish Armada was a success or the Russian Revolution was crushed in 1918 — and he will transfer fragments of this world to the history books whenever possible. Much of the propagandist writing of our time amounts to plain forgery. Material facts are suppressed, dates altered, quotations removed from their context and doctored so as to change their meaning. Events which it is felt ought not to have happened are left unmentioned and ultimately denied(6). In 1927 Chiang Kai Shek boiled hundreds of Communists alive, and yet within ten years he had become one of the heroes of the Left. The re-alignment of world politics had brought him into the anti-Fascist camp, and so it was felt that the boiling of the Communists ‘didn't count’, or perhaps had not happened. The primary aim of propaganda is, of course, to influence contemporary opinion, but those who rewrite history do probably believe with part of their minds that they are actually thrusting facts into the past. When one considers the elaborate forgeries that have been committed in order to show that Trotsky did not play a valuable part in the Russian civil war, it is difficult to feel that the people responsible are merely lying. More probably they feel that their own version was what happened in the sight of God, and that one is justified in rearranging the records accordingly.
Indifference to objective truth is encouraged by the sealing-off of one part of the world from another, which makes it harder and harder to discover what is actually happening. There can often be a genuine doubt about the most enormous events. For example, it is impossible to calculate within millions, perhaps even tens of millions, the number of deaths caused by the present war. The calamities that are constantly being reported — battles, massacres, famines, revolutions — tend to inspire in the average person a feeling of unreality. One has no way of verifying the facts, one is not even fully certain that they have happened, and one is always presented with totally different interpretations from different sources. What were the rights and wrongs of the Warsaw rising of August 1944? Is it true about the German gas ovens in Poland? Who was really to blame for the Bengal famine? Probably the truth is discoverable, but the facts will be so dishonestly set forth in almost any newspaper that the ordinary reader can be forgiven either for swallowing lies or failing to form an opinion. The general uncertainty as to what is really happening makes it easier to cling to lunatic beliefs. Since nothing is ever quite proved or disproved, the most unmistakable fact can be impudently denied. Moreover, although endlessly brooding on power, victory, defeat, revenge, the nationalist is often somewhat uninterested in what happens in the real world. What he wants is to feel that his own unit is getting the better of some other unit, and he can more easily do this by scoring off an adversary than by examining the facts to see whether they support him. All nationalist controversy is at the debating-society level. It is always entirely inconclusive, since each contestant invariably believes himself to have won the victory. Some nationalists are not far from schizophrenia, living quite happily amid dreams of power and conquest which have no connection with the physical world.
I have examined as best as I can the mental habits which are common to all forms of nationalism. The next thing is to classify those forms, but obviously this cannot be done comprehensively. Nationalism is an enormous subject. The world is tormented by innumerable delusions and hatreds which cut across one another in an extremely complex way, and some of the most sinister of them have not yet impinged on the European consciousness. In this essay I am concerned with nationalism as it occurs among the English intelligentsia. In them, much more than in ordinary English people, it is unmixed with patriotism and therefore can be studied pure. Below are listed the varieties of nationalism now flourishing among English intellectuals, with such comments as seem to be needed. It is convenient to use three headings, Positive, Transferred, and Negative, though some varieties will fit into more than one category:
Positive Nationalism
(i) Neo-toryism. Exemplified by such people as Lord Elton, A. P. Herbert, G. M. Young, Professor Pickthorn, by the literature of the Tory Reform Committee, and by such magazines as the New English Review and the Nineteenth Century and After. The real motive force of neo-Toryism, giving it its nationalistic character and differentiating it from ordinary Conservatism, is the desire not to recognise that British power and influence have declined. Even those who are realistic enough to see that Britain's military position is not what it was, tend to claim that ‘English ideas’ (usually left undefined) must dominate the world. All neo-Tories are anti-Russian, but sometimes the main emphasis is anti-American. The significant thing is that this school of thought seems to be gaining ground among youngish intellectuals, sometimes ex-Communists, who have passed through the usual process of disillusionment and become disillusioned with that. The anglophobe who suddenly becomes violently pro-British is a fairly common figure. Writers who illustrate this tendency are F. A. Voigt, Malcolm Muggeridge, Evelyn Waugh, Hugh Kingsmill, and a psychologically similar development can be observed in T. S. Eliot, Wyndham Lewis, and various of their followers.
(ii) Celtic Nationalism. Welsh, Irish and Scottish nationalism have points of difference but are alike in their anti-English orientation. Members of all three movements have opposed the war while continuing to describe themselves as pro-Russian, and the lunatic fringe has even contrived to be simultaneously pro-Russian and pro-Nazi. But Celtic nationalism is not the same thing as anglophobia. Its motive force is a belief in the past and future greatness of the Celtic peoples, and it has a strong tinge of racialism. The Celt is supposed to be spiritually superior to the Saxon — simpler, more creative, less vulgar, less snobbish, etc. — but the usual power hunger is there under the surface. One symptom of it is the delusion that Eire, Scotland or even Wales could preserve its independence unaided and owes nothing to British protection. Among writers, good examples of this school of thought are Hugh McDiarmid and Sean O'Casey. No modern Irish writer, even of the stature of Yeats or Joyce, is completely free from traces of nationalism.
(iii) Zionism. This the unusual characteristics of a nationalist movement, but the American variant of it seems to be more violent and malignant than the British. I classify it under Direct and not Transferred nationalism because it flourishes almost exclusively among the Jews themselves. In England, for several rather incongruous reasons, the intelligentsia are mostly pro-Jew on the Palestine issue, but they do not feel strongly about it. All English people of goodwill are also pro-Jew in the sense of disapproving of Nazi persecution. But any actual nationalistic loyalty, or belief in the innate superiority of Jews, is hardly to be found among Gentiles.
Transferred Nationalism
(i) Communism.
(ii) Political Catholicism.
(iii) Colour Feeling. The old-style contemptuous attitude towards ‘natives’ has been much weakened in England, and various pseudo-scientific theories emphasising the superiority of the white race have been abandoned(7). Among the intelligentsia, colour feeling only occurs in the transposed form, that is, as a belief in the innate superiority of the coloured races. This is now increasingly common among English intellectuals, probably resulting more often from masochism and sexual frustration than from contact with the Oriental and Negro nationalist movements. Even among those who do not feel strongly on the colour question, snobbery and imitation have a powerful influence. Almost any English intellectual would be scandalised by the claim that the white races are superior to the coloured, whereas the opposite claim would seem to him unexceptionable even if he disagreed with it. Nationalistic attachment to the coloured races is usually mixed up with the belief that their sex lives are superior, and there is a large underground mythology about the sexual prowess of Negroes.
(iv) Class Feeling. Among upper-class and middle-class intellectuals, only in the transposed form — i. e. as a belief in the superiority of the proletariat. Here again, inside the intelligentsia, the pressure of public opinion is overwhelming. Nationalistic loyalty towards the proletariat, and most vicious theoretical hatred of the bourgeoisie, can and often do co-exist with ordinary snobbishness in everyday life.
(v) Pacifism. The majority of pacifists either belong to obscure religious sects or are simply humanitarians who object to the taking of life and prefer not to follow their thoughts beyond that point. But there is a minority of intellectual pacifists whose real though unadmitted motive appears to be hatred of western democracy and admiration of totalitarianism. Pacifist propaganda usually boils down to saying that one side is as bad as the other, but if one looks closely at the writings of younger intellectual pacifists, one finds that they do not by any means express impartial disapproval but are directed almost entirely against Britain and the United States. Moreover they do not as a rule condemn violence as such, but only violence used in defence of western countries. The Russians, unlike the British, are not blamed for defending themselves by warlike means, and indeed all pacifist propaganda of this type avoids mention of Russia or China. It is not claimed, again, that the Indians should abjure violence in their struggle against the British. Pacifist literature abounds with equivocal remarks which, if they mean anything, appear to mean that statesmen of the type of Hitler are preferable to those of the type of Churchill, and that violence is perhaps excusable if it is violent enough. After the fall of France, the French pacifists, faced by a real choice which their English colleagues have not had to make, mostly went over to the Nazis, and in England there appears to have been some small overlap of membership between the Peace Pledge Union and the Blackshirts. Pacifist writers have written in praise of Carlyle, one of the intellectual fathers of Fascism. All in all it is difficult not to feel that pacifism, as it appears among a section of the intelligentsia, is secretly inspired by an admiration for power and successful cruelty. The mistake was made of pinning this emotion to Hitler, but it could easily be retransfered.
Negative Nationalism
(i) Anglophobia. Within the intelligentsia, a derisive and mildly hostile attitude towards Britain is more or less compulsory, but it is an unfaked emotion in many cases. During the war it was manifested in the defeatism of the intelligentsia, which persisted long after it had become clear that the Axis powers could not win. Many people were undisguisedly pleased when Singapore fell ore when the British were driven out of Greece, and there was a remarkable unwillingness to believe in good news, e.g. el Alamein, or the number of German planes shot down in the Battle of Britain. English left-wing intellectuals did not, of course, actually want the Germans or Japanese to win the war, but many of them could not help getting a certain kick out of seeing their own country humiliated, and wanted to feel that the final victory would be due to Russia, or perhaps America, and not to Britain. In foreign politics many intellectuals follow the principle that any faction backed by Britain must be in the wrong. As a result, ‘enlightened’ opinion is quite largely a mirror-image of Conservative policy. Anglophobia is always liable to reversal, hence that fairly common spectacle, the pacifist of one war who is a bellicist in the next.
(ii) Anti-Semitism. There is little evidence about this at present, because the Nazi persecutions have made it necessary for any thinking person to side with the Jews against their oppressors. Anyone educated enough to have heard the word ‘antisemitism’ claims as a matter of course to be free of it, and anti-Jewish remarks are carefully eliminated from all classes of literature. Actually antisemitism appears to be widespread, even among intellectuals, and the general conspiracy of silence probably helps exacerbate it. People of Left opinions are not immune to it, and their attitude is sometimes affected by the fact that Trotskyists and Anarchists tend to be Jews. But antisemitism comes more naturally to people of Conservative tendency, who suspect Jews of weakening national morale and diluting the national culture. Neo-Tories and political Catholics are always liable to succumb to antisemitism, at least intermittently.
(iii) Trotskyism. This word is used so loosely as to include Anarchists, democratic Socialists and even Liberals. I use it here to mean a doctrinaire Marxist whose main motive is hostility to the Stalin regime. Trotskyism can be better studied in obscure pamphlets or in papers like the Socialist Appeal than in the works of Trotsky himself, who was by no means a man of one idea. Although in some places, for instance in the United States, Trotskyism is able to attract a fairly large number of adherents and develop into an organised movement with a petty fuerher of its own, its inspiration is essentially negative. The Trotskyist is against Stalin just as the Communist is for him, and, like the majority of Communists, he wants not so much to alter the external world as to feel that the battle for prestige is going in his own favour. In each case there is the same obsessive fixation on a single subject, the same inability to form a genuinely rational opinion based on probabilities. The fact that Trotskyists are everywhere a persecuted minority, and that the accusation usually made against them, i. e. of collaborating with the Fascists, is obviously false, creates an impression that Trotskyism is intellectually and morally superior to Communism; but it is doubtful whether there is much difference. The most typical Trotskyists, in any case, are ex-Communists, and no one arrives at Trotskyism except via one of the left-wing movements. No Communist, unless tethered to his party by years of habit, is secure against a sudden lapse into Trotskyism. The opposite process does not seem to happen equally often, though there is no clear reason why it should not.
In the classification I have attempted above, it will seem that I have often exaggerated, oversimplified, made unwarranted assumptions and have left out of account the existence of ordinarily decent motives. This was inevitable, because in this essay I am trying to isolate and identify tendencies which exist in all our minds and pervert our thinking, without necessarily occurring in a pure state or operating continuously. It is important at this point to correct the over-simplified picture which I have been obliged to make. To begin with, one has no right to assume that everyone, or even every intellectual, is infected by nationalism. Secondly, nationalism can be intermittent and limited. An intelligent man may half-succumb to a belief which he knows to be absurd, and he may keep it out of his mind for long periods, only reverting to it in moments of anger or sentimentality, or when he is certain that no important issues are involved. Thirdly, a nationalistic creed may be adopted in good faith from non-nationalistic motives. Fourthly, several kinds of nationalism, even kinds that cancel out, can co-exist in the same person.
All the way through I have said, ‘the nationalist does this’ or ‘the nationalist does that’, using for purposes of illustration the extreme, barely sane type of nationalist who has no neutral areas in his mind and no interest in anything except the struggle for power. Actually such people are fairly common, but they are not worth the powder and shot. In real life Lord Elton, D. N. Pritt, Lady Houston, Ezra Pound, Lord Vanisttart, Father Coughlin and all the rest of their dreary tribe have to be fought against, but their intellectual deficiencies hardly need pointing out. Monomania is not interesting, and the fact that no nationalist of the more bigoted kind can write a book which still seems worth reading after a lapse of years has a certain deodorising effect. But when one has admitted that nationalism has not triumphed everywhere, that there are still peoples whose judgements are not at the mercy of their desires, the fact does remain that the pressing problems — India, Poland, Palestine, the Spanish civil war, the Moscow trials, the American Negroes, the Russo-German Pact or what have you — cannot be, or at least never are, discussed upon a reasonable level. The Eltons and Pritts and Coughlins, each of them simply an enormous mouth bellowing the same lie over and over again, are obviously extreme cases, but we deceive ourselves if we do not realise that we can all resemble them in unguarded moments. Let a certain note be struck, let this or that corn be trodden on — and it may be corn whose very existence has been unsuspected hitherto — and the most fair-minded and sweet-tempered person may suddenly be transformed into a vicious partisan, anxious only to ‘score’ over his adversary and indifferent as to how many lies he tells or how many logical errors he commits in doing so. When Lloyd George, who was an opponent of the Boer War, announced in the House of Commons that the British communiques, if one added them together, claimed the killing of more Boers than the whole Boer nation contained, it is recorded that Arthur Balfour rose to his feet and shouted ‘Cad!’ Very few people are proof against lapses of this type. The Negro snubbed by a white woman, the Englishman who hears England ignorantly criticised by an American, the Catholic apologist reminded of the Spanish Armada, will all react in much the same way. One prod to the nerve of nationalism, and the intellectual decencies can vanish, the past can be altered, and the plainest facts can be denied.
If one harbours anywhere in one's mind a nationalistic loyalty or hatred, certain facts, although in a sense known to be true, are inadmissible. Here are just a few examples. I list below five types of nationalist, and against each I append a fact which it is impossible for that type of nationalist to accept, even in his secret thoughts:
BRITISH TORY: Britain will come out of this war with reduced power and prestige.COMMUNIST: If she had not been aided by Britain and America, Russia would have been defeated by Germany.IRISH NATIONALIST: Eire can only remain independent because of British protection.TROTSKYIST: The Stalin regime is accepted by the Russian masses.PACIFIST: Those who ‘abjure’ violence can only do so because others are committing violence on their behalf.
All of these facts are grossly obvious if one's emotions do not happen to be involved: but to the kind of person named in each case they are also intolerable, and so they have to be denied, and false theories constructed upon their denial. I come back to the astonishing failure of military prediction in the present war. It is, I think, true to say that the intelligentsia have been more wrong about the progress of the war than the common people, and that they were more swayed by partisan feelings. The average intellectual of the Left believed, for instance, that the war was lost in 1940, that the Germans were bound to overrun Egypt in 1942, that the Japanese would never be driven out of the lands they had conquered, and that the Anglo-American bombing offensive was making no impression on Germany. He could believe these things because his hatred for the British ruling class forbade him to admit that British plans could succeed. There is no limit to the follies that can be swallowed if one is under the influence of feelings of this kind. I have heard it confidently stated, for instance, that the American troops had been brought to Europe not to fight the Germans but to crush an English revolution. One has to belong to the intelligentsia to believe things like that: no ordinary man could be such a fool. When Hitler invaded Russia, the officials of the MOI issued ‘as background’ a warning that Russia might be expected to collapse in six weeks. On the other hand the Communists regarded every phase of the war as a Russian victory, even when the Russians were driven back almost to the Caspian Sea and had lost several million prisoners. There is no need to multiply instances. The point is that as soon as fear, hatred, jealousy and power worship are involved, the sense of reality becomes unhinged. And, as I have pointed out already, the sense of right and wrong becomes unhinged also. There is no crime, absolutely none, that cannot be condoned when ‘our’ side commits it. Even if one does not deny that the crime has happened, even if one knows that it is exactly the same crime as one has condemned in some other case, even if one admits in an intellectual sense that it is unjustified — still one cannot feel that it is wrong. Loyalty is involved, and so pity ceases to function.
The reason for the rise and spread of nationalism is far too big a question to be raised here. It is enough to say that, in the forms in which it appears among English intellectuals, it is a distorted reflection of the frightful battles actually happening in the external world, and that its worst follies have been made possible by the breakdown of patriotism and religious belief. If one follows up this train of thought, one is in danger of being led into a species of Conservatism, or into political quietism. It can be plausibly argued, for instance — it is even possibly true — that patriotism is an inoculation against nationalism, that monarchy is a guard against dictatorship, and that organised religion is a guard against superstition. Or again, it can be argued that no unbiased outlook is possible, that all creeds and causes involve the same lies, follies, and barbarities; and this is often advanced as a reason for keeping out of politics altogether. I do not accept this argument, if only because in the modern world no one describable as an intellectual can keep out of politics in the sense of not caring about them. I think one must engage in politics — using the word in a wide sense — and that one must have preferences: that is, one must recognise that some causes are objectively better than others, even if they are advanced by equally bad means. As for the nationalistic loves and hatreds that I have spoken of, they are part of the make-up of most of us, whether we like it or not. Whether it is possible to get rid of them I do not know, but I do believe that it is possible to struggle against them, and that this is essentially a moral effort. It is a question first of all of discovering what one really is, what one's own feelings really are, and then of making allowance for the inevitable bias. If you hate and fear Russia, if you are jealous of the wealth and power of America, if you despise Jews, if you have a sentiment of inferiority towards the British ruling class, you cannot get rid of those feelings simply by taking thought. But you can at least recognise that you have them, and prevent them from contaminating your mental processes. The emotional urges which are inescapable, and are perhaps even necessary to political action, should be able to exist side by side with an acceptance of reality. But this, I repeat, needs a moral effort, and contemporary English literature, so far as it is alive at all to the major issues of our time, shows how few of us are prepared to make it.
1945
_____1) Nations, and even vaguer entities such as Catholic Church or the proleteriat, are commonly thought of as individuals and often referred to as ‘she’. Patently absurd remarks such as ‘Germany is naturally treacherous’ are to be found in any newspaper one opens and reckless generalization about national character (‘The Spaniard is a natural aristocrat’ or ‘Every Englishman is a hypocrite’) are uttered by almost everyone. Intermittently these generalizations are seen to be unfounded, but the habit of making them persists, and people of professedly international outlook, e.g., Tolstoy or Bernard Shaw, are often guilty of them.[back]2) A few writers of conservative tendency, such as Peter Drucker, foretold an agreement between Germany and Russia, but they expected an actual alliance or amalgamation which would be permanent. No Marxist or other left-wing writer, of whatever colour, came anywhere near foretelling the Pact. [back]3) The military commentators of the popular press can mostly be classified as pro-Russian or anti-Russianm pro-blimp or anti-blimp. Such errors as believing the Mrginot Line impregnable, or predicting that Russia would conquer Germany in three months, have failed to shake their reputation, because they were always saying what their own particular audience wanted to hear. The two military critics most favoured by the intelligentsia are Captain Liddell Hart and Major-General Fuller, the first of whom teachs that the defence is stronger that the attack, and the second that the attack is stronger that the defence. This contradiction has not prevented both of them from being accepted as authorities by the sme public. The secret reason for their vogue in left-wing circles is that both of them are at odds with the War Office. [back]4) Certain Americans have expressed dissatisfaction because ‘Anglo-American’ is the form of combination for these two words. It has been proposed to submite ‘Americo-British’. [back]5) The News Chronicle advised its readers to visit the news film at which the entire execution could be witnessed, with close-ups. The Star published with seeming approval photographs of nearly naked female collaborationists being baited by the Paris mob. These photographs had a marked resemblance to the Nazi photographs of Jews being baited by the Berlin mob. [back]6) En example is the Russo-German Pact, which is being effaced as quickly as possible from public memory. A Russian correspondent informs me that mention of the Pact is already being omitted from Russian year-books which table recent political events. [back]7) A good example is the sunstroke superstition. Until recently it was believed that the white races were much more liable to sunstroke that the coloured, and that a white man could not safely walk about in tropical sunshine without a pith helmet. There was no evidence whatever for this theory, but it served the purpose of accentuating the difference between ‘natives’ and Europeans. During the war the theory was quietly dropped and whole armies manoeuvred in the tropics without pith helmets. So long as the sunstroke superstition survived, English doctors in India appear to have believed in it as firmly as laymen. [back]
THE END
____BD____
George Orwell: ‘Notes on Nationalism’
First published: Polemic. — GB, London. — May 1945.
George Orwell: ‘Notes on Nationalism’
First published: Polemic. — GB, London. — May 1945.
- Reprinted:
- — ‘England Your England and Other Essays’. — 1953.
Subscribe to:
Posts (Atom)